
Unlocking the Legacy: Gupta Empire Achievements Reveale
Table of Contents
Introduction
Delve into the fascinating history of the Gupta Empire and uncover the remarkable achievements that shaped ancient India’s cultural economic landscape. From trade to education, the Gupta dynasty left an indelible mark that resonates even today.
Gupta Empire: A Brief Overview
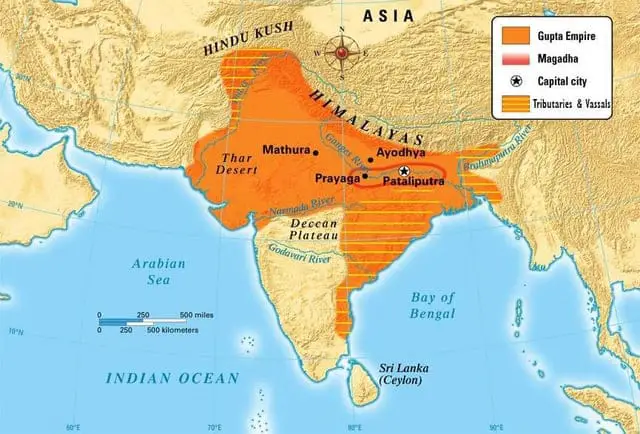
The Gupta Empire, also known as the Golden Age of India, reigned from around 320 to 550 CE. It was a time marked by immense prosperity and cultural flourishing, with significant advancements in various fields.
The Gupta Empire, a significant period in ancient Indian history, flourished from around the 4th to the 6th century CE. This golden age of Indian civilization left an indelible mark on the cultural, social, and political landscape of the subcontinent. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of the Gupta Empire and explore its remarkable achievements.
The Gupta Empire, founded by Maharaja Sri Gupta, emerged in Magadha (present-day Bihar, India) and gradually expanded its influence across northern and central India. Under the Gupta rulers, the empire reached its zenith, characterized by advancements in arts, sciences, literature, and mathematics.

One of the most notable Gupta rulers was Chandragupta I, who ascended the throne around 320 CE. His reign marked the beginning of the Gupta era, and he laid the foundation for a prosperous empire that would endure for centuries to come. Chandragupta I’s successors, such as Samudragupta and Chandragupta II (also known as Vikramaditya), further consolidated and expanded Gupta rule.
The Gupta Empire was renowned for its patronage of the arts and learning. During this period, the empire witnessed a remarkable flourishing of Indian culture, with advancements in architecture, sculpture, painting, and literature. The Ajanta and Ellora caves stand as exceptional examples of Gupta-era rock-cut architecture, adorned with exquisite sculptures and intricate murals that depict scenes from mythology and daily life.
In the field of literature, the Gupta period witnessed the composition of several literary masterpieces. The playwright Kalidasa, renowned for his works like “Shakuntala” and “Meghaduta,” flourished during this time. His plays are still celebrated for their poetic beauty and captivating storytelling.
The Gupta Empire also made significant contributions to the field of mathematics. The mathematician Aryabhata, belonging to the Gupta period, devised the concept of zero and the decimal place value system. His groundbreaking works laid the foundation for modern-day mathematics and greatly influenced scholars in the East and West.
The Gupta rulers were not only patrons of the arts and sciences but also adept administrators. They established efficient governance systems and promoted trade and commerce. The Gupta Empire thrived economically, with flourishing trade routes connecting India to various parts of the world. This facilitated cultural exchanges and the spread of Indian knowledge and ideas.
However, like any empire, the Gupta Empire faced its own set of challenges. Internal conflicts, invasions, and regional fragmentation eventually led to its decline. By the mid-6th century, the Gupta Empire had disintegrated, leaving behind a legacy that would continue to inspire generations to come.
Gupta Empire Achievements
The Gupta Empire, left an indelible mark on the subcontinent’s history. This period of prosperity witnessed remarkable advancements in various fields, including arts, sciences, literature, and governance. Let’s take a closer look at the achievements of the Gupta Empire.
One of the Gupta Empire’s notable achievements was its patronage of the arts. During this golden era, Indian culture flourished, and artistic endeavors reached new heights. The Gupta rulers were great supporters of architecture, resulting in the construction of magnificent temples and monuments that stood as testaments to their grandeur. These architectural marvels showcased intricate carvings, elaborate sculptures, and stunning designs.
The Gupta Empire also made significant contributions to the field of science. Scholars and scientists of this era made remarkable progress in fields such as astronomy, mathematics, and medicine. They developed sophisticated mathematical concepts, including the concept of zero and the decimal system, which revolutionized mathematics worldwide. Additionally, Gupta scientists made remarkable strides in the field of astronomy, with important discoveries and advancements in celestial observations.
Literature and poetry also thrived during the Gupta Empire. The era gave birth to some of the most celebrated works of Indian literature. The renowned playwright Kalidasa, known for his poetic masterpieces, produced captivating plays, such as “Shakuntala” and “Meghaduta.” These works continue to be cherished for their eloquence and timeless storytelling.

The Gupta Empire’s achievements were not limited to the arts and sciences. The rulers of this dynasty were also known for their effective governance and administrative skills. They established a well-structured system that ensured stability and prosperity within the empire. The Gupta rulers promoted trade and commerce, resulting in economic growth and the establishment of strong trade networks with neighboring regions.
Furthermore, the Gupta Empire’s cultural influence extended beyond its borders. It served as a center for learning and attracted scholars and intellectuals from far and wide. This led to the exchange of ideas, knowledge, and cultural practices, enriching not only the Gupta Empire but also the regions that interacted with it.
Despite its impressive achievements, the Gupta Empire faced challenges that eventually led to its decline. Internal conflicts, invasions, and regional fragmentation weakened the empire, ultimately leading to its dissolution. However, the legacy of the Gupta Empire continues to inspire and influence generations, leaving an enduring impact on Indian history and civilization.
- Art and Architecture: The Gupta period witnessed a renaissance in art and architecture, evident in the intricate sculptures and magnificent temples that still stand today.
- Science and Mathematics: Gupta scholars made groundbreaking contributions to mathematics, with the concept of zero and the decimal system originating during this time.
- Literature: Sanskrit literature flourished under Gupta patronage, with famous works like the Kama Sutra and Kalidasa’s plays enriching the cultural tapestry.
- Administrative Excellence: The Gupta rulers were known for their efficient governance and diplomatic skills, ensuring a stable and prosperous empire.
Legacy of Gupta Traders
Gupta traders played a crucial role in facilitating trade between India and other regions. Their expertise in commerce and navigation helped establish lucrative trade routes that connected India to the rest of the world.
Educational Institutions During Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was home to renowned centers of learning, such as Nalanda University. Scholars from far and wide flocked to these institutions to study a wide range of subjects, from philosophy to medicine.
During the Gupta Empire’s reign in ancient India, education played a vital role in shaping society and fostering intellectual growth. The Gupta rulers recognized the importance of knowledge and established educational institutions that became centers of learning and enlightenment. Let us delve into the educational landscape of the Gupta Empire and explore the impact it had on the development of Indian education.
The Gupta Empire, which thrived from the 4th to the 6th century CE, witnessed a remarkable emphasis on education. The rulers recognized that education was the key to progress and prosperity, and therefore, they actively supported the establishment of educational institutions across their empire.

One of the notable institutions during this period was the Nalanda University. Founded during the Gupta era, Nalanda University was renowned as a center of excellence for higher education. Scholars from far and wide flocked to Nalanda to study a wide range of subjects, including philosophy, mathematics, medicine, astronomy, and literature. The university boasted a vast library that housed thousands of manuscripts and attracted students from various parts of the world.
Another prominent educational institution was the Taxila University. Situated in present-day Pakistan, Taxila University was a renowned seat of learning during the Gupta Empire. It attracted students from different regions, fostering a multicultural and intellectually vibrant environment. The university offered courses in various disciplines, including mathematics, medicine, grammar, philosophy, and warfare strategies.
The educational system during the Gupta Empire was primarily centered around the Gurukula system. Under this system, students lived with their teachers and received education in a holistic manner. Teachers imparted knowledge not only in the subjects of study but also in ethics, morals, and social values. This close teacher-student relationship fostered a deep sense of respect and reverence for knowledge.
The curriculum during this time focused on a wide range of subjects. Students were taught languages such as Sanskrit and Prakrit, as well as subjects like mathematics, astronomy, philosophy, and literature. Practical skills were also valued, with training in fields such as agriculture, architecture, and metallurgy.
Scholars and teachers held esteemed positions in society during the Gupta Empire. They were respected for their knowledge and wisdom, and their contributions to education were highly valued. Many scholars wrote treatises and commentaries on various subjects, enriching the body of knowledge during that time.
The Gupta Empire’s emphasis on education had a profound impact on society. It led to the development of a learned and intellectual class, fostering a culture of intellectual curiosity and innovation. The knowledge disseminated through educational institutions helped in the advancement of various fields, including science, mathematics, medicine, and literature.
However, it is important to note that education during this period was primarily accessible to the privileged classes, such as the nobles and the Brahmin caste. The education of women and lower castes was limited during this time. Nonetheless, the Gupta Empire’s focus on education laid the foundation for future educational systems in India.
Gupta Empire’s Infrastructure Development
Under the Gupta rulers, the empire witnessed significant infrastructure development, with the construction of well-planned cities, intricate road networks, and efficient water management systems. These advancements laid the foundation for India’s future growth.
The Gupta rulers recognized the importance of infrastructure development in building a strong and prosperous society. In this article, we will delve into the infrastructure development during the Gupta Empire and its impact on the growth of the Indian subcontinent.
The Gupta Empire was renowned for its impressive infrastructure. The rulers invested heavily in building roads, bridges, canals, and other public works that connected different parts of the empire. The roads were well-maintained and facilitated trade and communication between different regions. They also allowed the rapid deployment of troops during times of war.

One of the most notable infrastructure projects during this period was the Grand Trunk Road. Built during the reign of Chandragupta II, the Grand Trunk Road stretched from Peshawar in present-day Pakistan to Chittagong in present-day Bangladesh. The road was over 2,500 kilometers long and facilitated trade and commerce between different parts of the empire. The road also served as a vital link between India and Central Asia, promoting cultural exchange and the spread of ideas.
The Gupta Empire was also renowned for its water management systems. The rulers built numerous reservoirs, canals, and wells that irrigated the farmlands and provided drinking water to the people. One of the most impressive water management systems was the Sudarshana Lake. Built during the reign of Chandragupta II, the Sudarshana Lake was a massive artificial lake that covered an area of over 200 hectares. The lake was used for irrigation and fish farming and provided drinking water to the nearby towns and villages.
The Gupta Empire also invested in building impressive architectural structures. The famous Iron Pillar of Delhi, which still stands today, was built during this period. The pillar is over 7 meters tall and weighs around 6 tons. It is made of wrought iron and has stood for over 1,600 years without rusting. The Gupta rulers also built numerous temples, palaces, and forts that served as symbols of their power and authority.
The infrastructure development during the Gupta Empire had a profound impact on society. It facilitated trade and commerce, promoted cultural exchange, and provided the people with basic amenities such as water and roads. The infrastructure also played a crucial role in the defense of the empire, allowing the rapid deployment of troops during times of war.
Conclusion
The Gupta Empire achievements continue to inspire awe and admiration, showcasing the rich cultural heritage of ancient India. As we reflect on their legacy, let us carry forward the spirit of innovation and excellence that defined this illustrious dynasty.
Take a journey through time and explore the wonders of the Gupta Empire, where prosperity and culture intertwined to create a Golden Age that still captivates us today. Join us in celebrating the legacy of this remarkable dynasty and discover the enduring Gupta Empire achievements that continue to shape India’s history.
Sources :

